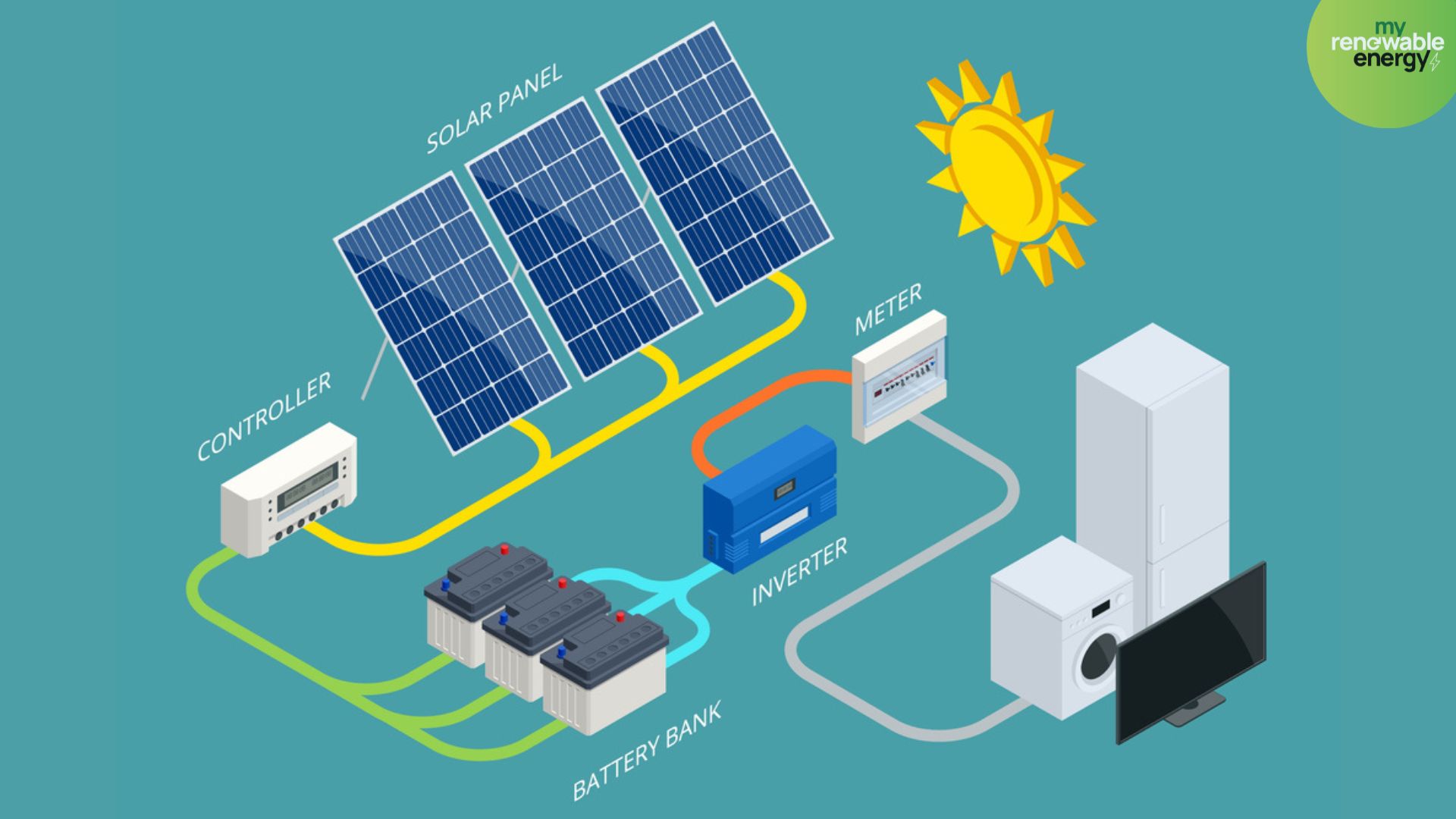
.jpg)
Solar Panel with Battery Storage – Everything You Should Know!
Solar panel systems have become increasingly popular in recent years, revolutionising the way we generate and consume electricity.
The integration of battery storage with solar panels has further enhanced the benefits of this green energy source.
But what exactly is solar panel battery storage, and how does it work? This is a way to save extra electricity produced by solar panels.
It works by converting sunlight into power and storing it in batteries. This stored energy can be used later, like when it's dark outside or there's a power outage.
Lets get into more details in this article, including its advantages and disadvantages, different types, recommended sizes in the UK, cost implications, and important factors to consider.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of batteries and determine if it is the right fit for your home.
What is solar panel with battery storage?
This is a way to collect and keep sunlight to use as power in your home or business.
Solar panels are devices that capture light from the sun and change it into electricity that we can use to power things like lights, TVs, and fridges.
Normally, this electricity is used up straight away. But, with a battery storage system, you can save this energy to use later on.
Battery and solar panel integration means that any extra electricity your solar panels make during the day doesn't go to waste.
Instead, you can store it and then use it at night or on cloudy days when your panels aren't getting much sunlight.
This setup is really handy because it makes you less dependent on buying electricity from companies, which can save you money and help the environment by using less fossil fuel energy.
Using these also means you don't have to worry as much about power cuts.
Since you've got your own supply of electricity saved up, you can keep your lights on even when there's a problem with the main power lines.
It's a smart choice for people wanting to make their homes or businesses more green and self-sufficient.
How Does a Solar Battery Work?
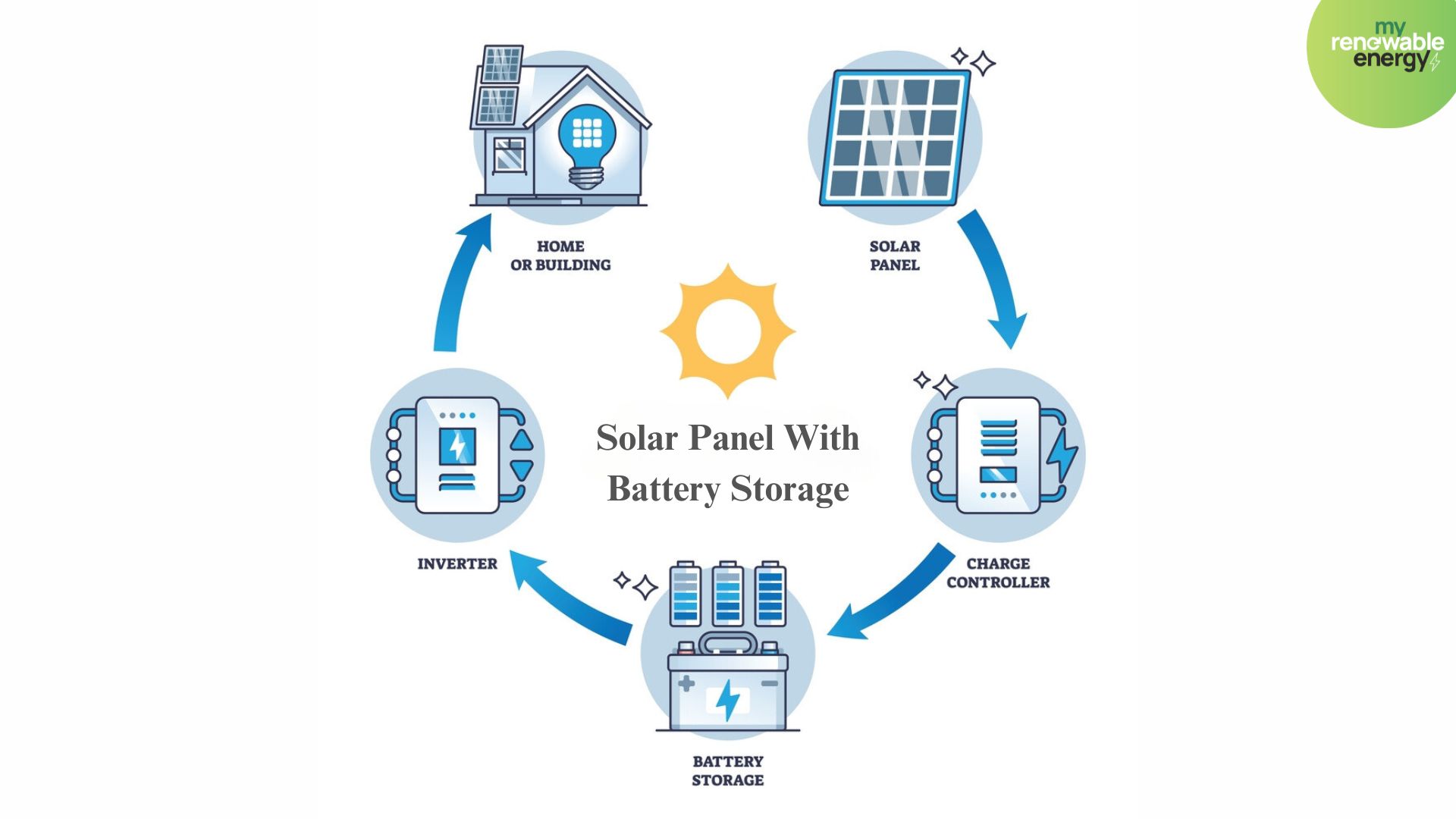
A solar battery works by storing sunlight as electrical energy so that it can be used later. This is especially useful when the sun isn't shining, like at night or on a cloudy day. Here's a simple breakdown of how it happens:
-
Collecting Sunlight: Solar panels are made up of tiny units called solar cells. These cells are designed to catch sunlight and turn it into electricity. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect. These are usually fitted on rooftops or other areas where they can get a lot of sun.
-
Converting Energy: The electricity that the solar cells create is in a form called direct current (DC). Most homes and appliances use a different type of electricity called alternating current (AC). So, the system uses an inverter to change the DC electricity into AC electricity that we can use.
-
Storing Energy: This is where the battery comes in. Not all the electricity produced during the day is needed straight away. The battery stores this extra electricity. It’s like a big rechargeable battery that you might use in gadgets around the house, but much larger and more powerful.
-
Using the Stored Energy: When your solar panels aren’t making electricity (like at night), the battery can provide the stored energy to power your home. This means that instead of buying electricity from the grid when your panels aren't working, you can use what you've stored.
-
Managing the System: Modern solar batteries often come with smart technology that decides the best time to store energy and when to use it, making the most out of the sunlight and saving costs.
By using these, homes and businesses can be less reliant on external electricity supplies, save money on energy bills, and help the environment by using clean, renewable energy.
Exploring Various Types of Solar Batteries
There are several types available, each with its own set of characteristics and advantages.
Let's look into the different types, including lead-acid, lithium-ion, saltwater, and flow batteries, that are commonly used in these systems.
-
Lead-Acid Batteries
These are the traditional and most common type. They are affordable but have a shorter lifespan compared to other types.
These batteries require regular maintenance, such as monitoring and adjusting electrolyte levels.
While they are cost-effective, these can be sensitive to temperature fluctuations and require proper ventilation.
Despite these drawbacks, they have been widely used for years in solar power systems due to their initial affordability.
-
Lithium-Ion Batteries
They have gained popularity in recent years due to their higher energy density, longer lifespan, and lower maintenance requirements.
These batteries use advanced lithium-ion technology, providing a higher storage capacity and efficiency than lead-acid batteries.
These are known for their lightweight properties, compact design, and longer cycle life.
Although they have a higher upfront cost, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
-
Saltwater Batteries
They offer a newer and more environmentally friendly alternative. These use saltwater as an electrolyte, eliminating the need for hazardous chemicals.
While still less commonly used compared to lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries, these have an advantage in terms of a longer lifespan and higher temperature tolerance.
They are considered safer and more sustainable as they do not contain toxic materials.
However, these generally have lower energy density and efficiency compared to lithium-ion batteries.
-
Flow Batteries
These are another type of energy storage technology. They consist of two tanks of electrolytes that flow through a membrane, creating a chemical reaction that generates electricity.
They offer advantages such as scalability, long lifespan, and the ability to store large amounts of energy.
They are particularly suitable for applications requiring high energy capacity and long-term storage solutions.
While flow batteries have higher upfront costs and larger footprints, they are known for their durability and performance.
By understanding the distinctions between lead-acid, lithium-ion, saltwater, and flow batteries, you can make an informed decision based on your specific requirements.
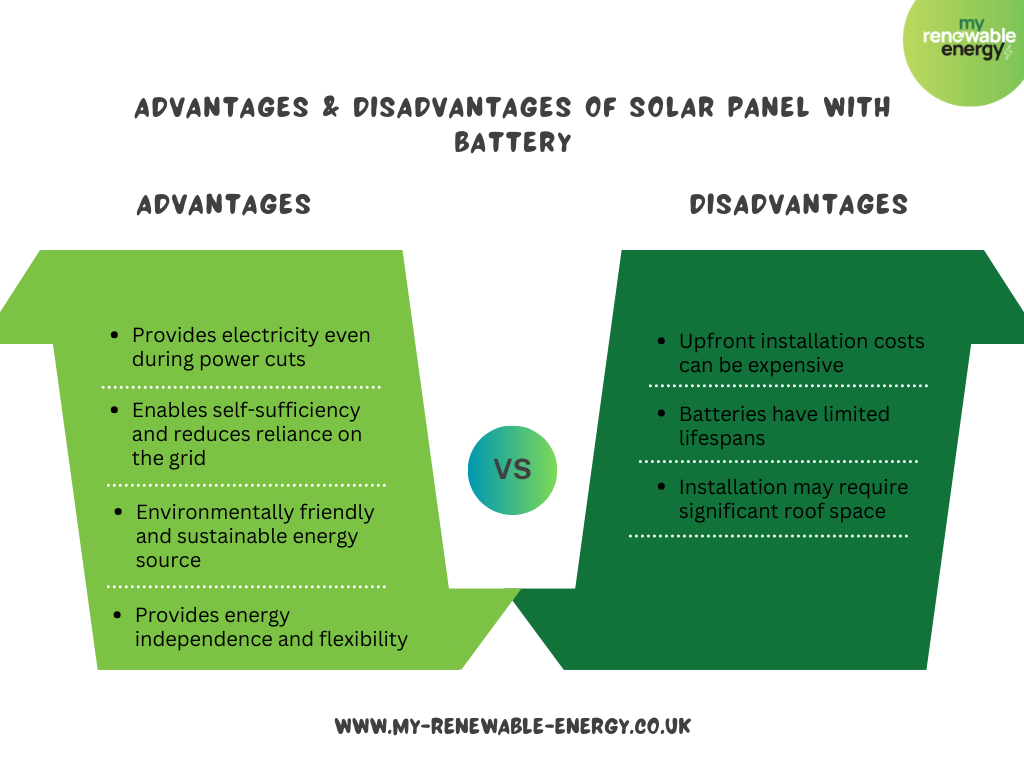
Advantages of Solar Panel with Battery
Below are some of the advantages of installing solar panels with batteries:
- Increased Energy Self-Sufficiency:
These batteries allow users to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during periods of low solar production.
This reduces reliance on the grid and increases energy self-sufficiency.
- Potential Cost Savings:
By storing and using their own solar-generated energy, users can reduce their reliance on grid electricity and potentially save money on their electricity bills over the long term.
- Peak Rate Optimisation:
It enables them to take advantage of time-of-use tariffs by using stored energy during peak rate periods.
This can lead to further cost savings by avoiding higher electricity rates during certain times of the day.
- Backup Power during Outages:
These systems provide a reliable source of backup power during power outages. This ensures continuity of essential services and appliances in the home, even when the grid is down.
- Reduction in Carbon Footprint:
By using stored energy from solar panels, users decrease their reliance on fossil fuel-based electricity from the grid, resulting in a reduced carbon footprint and a more sustainable energy consumption model.
- Longer Lifespan of Lithium-ion Batteries:
Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in these storage systems, have a longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
This means they can enjoy reliable energy storage for a longer period before requiring replacement.
Disadvantages
Below are some of the disadvantages that you need to keep in mind.
- High Initial Cost:
The initial cost of installing these can be relatively high, which may deter some homeowners despite the long-term cost savings.
However, prices are gradually decreasing as the technology advances and becomes more accessible.
- Battery Lifespan and Replacement:
While lithium-ion batteries have longer lifespans, they will still need to be replaced eventually, typically within 10-15 years.
This can add to the overall cost of the system in the long run.
- Installation May Require Substantial Roof Space:
Installing these generally necessitates a suitable amount of roof space.
This can pose a challenge for properties with limited roof area or multiple obstructions, such as chimneys or ventilation systems.
What is the recommended size of a solar battery in the UK?

In the UK, the size depends on various factors such as the size of the property, capacity of the solar panel system, and energy consumption patterns.
The size required for a three-bedroom home can vary and may benefit from a 5-6 kilowatt-hours (kWh) battery.
A smaller one-bedroom home might only need a 2-kWh battery, while a larger four-bedroom home might need a 9.5 kWh battery.
The size needed is also influenced by the size of the system. For example, a 4 kWp system needs an 8-9 kWh battery, while a 10 kWp system needs a 20-21 kWh battery.
However, it's important to note that sizing and panel array size are not rigidly interconnected, and each can be independently determined based on specific requirements.
It is common for professional installers to gather information from the customer regarding their energy usage and consumption patterns to design a system that maximises efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
To determine the appropriate size for a specific property, it is recommended to calculate the energy needs and consult professionals.
Considerations like the size of the property, capacity of the system, and energy usage patterns are essential in choosing the right size for efficient storage and utilisation of solar energy.
Important factors to consider

Before you get these, there are important things to consider. These factors include the size and capacity, how long the warranty lasts and how long it will work, if it works with your panels, the installation requirements, and any discounts or rebates available. Research and understand these factors before deciding.
Think about the size and capacity. Consider how much energy it can store and for how long. If you want more energy and longer backup power, you may need a bigger battery.
Check the warranty and expected lifespan. A longer warranty can give you more confidence in its quality.
Make sure it is compatible with your panels. Some batteries may not work with certain types or brands, so check before you buy.
Consider how it will be installed. Some require professional installation, while others can be installed by yourself. Think about the cost and difficulty of installation.
Lastly, look for any discounts or rebates available. Some places offer financial assistance to reduce the cost of buying and installing them.
Considering these factors will help you choose the right storage system for your needs and budget.
FAQs:
Can I save money with a solar battery?
Many users can save money with these. You can store extra energy when not much is being used and then use it when electricity prices are higher.
This way, you don't have to depend as much on energy from the power grid, and you can lower your electricity bills.
But whether this one is a good deal depends on things like how much energy you use, how much electricity costs, and how much it costs to install.
It's important to figure out how much money you could save and how long it will take to pay off the cost before deciding if it's worth it.
Is it worth getting a battery with solar panels?
Deciding whether to get them with solar panels depends on your energy goals, electricity consumption patterns, and the cost-effectiveness of the system.
If you want to be more self-sufficient and maybe save money on your electricity bills, then a battery could be a good investment.
Can I run my house on a solar battery?
While it is technically possible to run a house solely on them, it requires careful consideration of your energy consumption, available sunlight, and the capacity of the system.
Most users use a combination of solar power, stored energy, and grid electricity to ensure a continuous power supply.
How much does a solar panel battery cost in the UK?
The cost depends on various factors such as the size, capacity, brand, and type. On average, prices can range from £2,000 to £10,000, including installation costs.
It is recommended to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers and consider the long-term savings potential before making a purchase.
Final Thoughts!
Solar panel battery storage is a good way for users to make the most of solar energy.
It lets you store extra energy from your solar panels, which means you can use it later when you need it.
This helps you be more self-sufficient and could save you money on your electricity bills.
But before you decide to get them, think about how much energy you use, how much it costs, and what your long-term energy goals are.
Posted on Mar 19, 2024.
Back to News